Examples
Test cases are available in the
PyFR-Test-Cases <https://github.com/PyFR/PyFR-Test-Cases>
repository. It is important to note, however, that these examples
are all relatively small 2D simulations and, as such, are not
suitable for scalability or performance studies.
Euler Equations
2D Euler Vortex
Proceed with the following steps to run a parallel 2D Euler vortex
simulation on a structured mesh:
Navigate to the PyFR-Test-Cases/2d-euler-vortex
Run pyfr to convert the Gmsh
mesh file into a PyFR mesh file called 2d-euler-vortex.pyfrm
Run pyfr to partition the PyFR mesh file into two pieces:
Run pyfr to solve the Euler equations on the mesh, generating a
series of PyFR solution files called 2d-euler-vortex*.pyfrs
Run pyfr on the solution file 2d-euler-vortex-100.0.pyfrs 2d-euler-vortex-100.0.vtu
Visualise the unstructured VTK file in Paraview
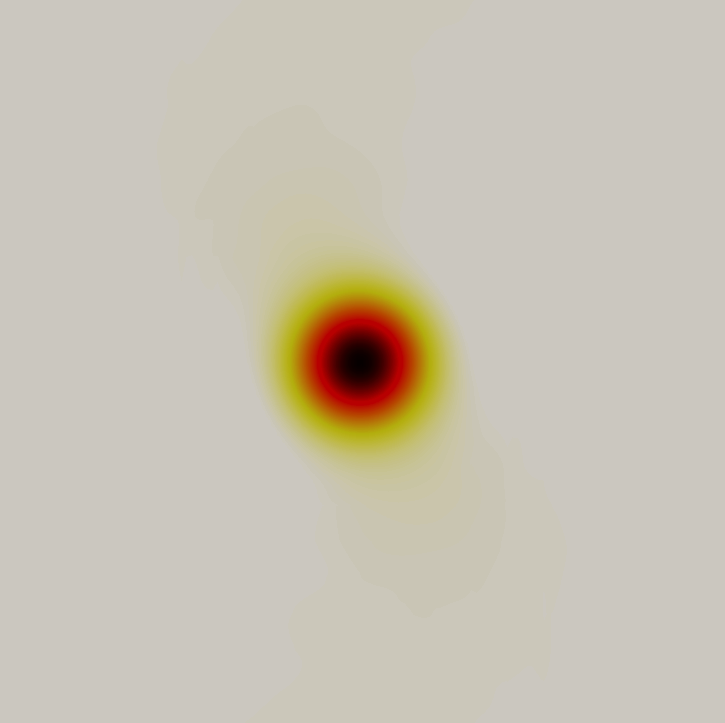
Colour map of density distribution at 100 time units.
Compressible Navier–Stokes Equations
2D Couette Flow
Proceed with the following steps to run a serial 2D Couette flow
simulation on a mixed unstructured mesh:
Navigate to the PyFR-Test-Cases/2d-couette-flow
Run pyfr to covert the Gmsh
mesh file into a PyFR mesh file called 2d-couette-flow.pyfrm
Run pyfr to solve the Navier-Stokes equations on the mesh,
generating a series of PyFR solution files called
2d-couette-flow-*.pyfrs
Run pyfr on the solution file 2d-couette-flow-040.pyfrs 2d-couette-flow-040.vtu
Visualise the unstructured VTK file in Paraview
Colour map of steady-state density distribution.
Incompressible Navier–Stokes Equations
2D Incompressible Cylinder Flow
Proceed with the following steps to run a serial 2D incompressible cylinder
flow simulation on a mixed unstructured mesh:
Navigate to the PyFR-Test-Cases/2d-inc-cylinder
Run pyfr to covert the Gmsh
mesh file into a PyFR mesh file called 2d-inc-cylinder.pyfrm
Run pyfr to solve the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations on the mesh,
generating a series of PyFR solution files called
2d-inc-cylinder-*.pyfrs
Run pyfr on the solution file 2d-inc-cylinder-75.00.pyfrs 2d-inc-cylinder-75.00.vtu
Visualise the unstructured VTK file in Paraview
Colour map of velocity magnitude distribution at 75 time units.